深入php面向对象、模式与实践
1 语法
1.1 基础语法
clone需要操作原对象,但又不想影响原对象.
$K_back = clone $K;基本数据类型和数组都为真复制,即为真副本,当属性为对象时,为假复制,改变副本仍会影响原对象.解决方案:
//在原对象中添加 function __clone(){ $this->对象 = clone $this->对象 }__clone在clone前自动触发,可以执行一些在备份前的属性操作.&传递引用方法引用传递,改变源对象
function set_K(& $K){...} function & get_K(){...}static延迟静态绑定应用场景:Dog类和Person类都需要一个返回实例化的方法,Dog类和Person类都继承于Animal抽象类.
abstract class Animal{ public static function create(){ //实例化调用类 return new static(); } } class Person extends Animal{...} //返回Person实例化类 Person::create();拦截器__get($property),访问未定义的属性时调用.__set($property,$value),给未定义的属性赋值时被调用.__isset($property),对未定义属性调用isset()方法时调用.__unset($property),对未定义属性调用unset()方法时调用.__call($method,$arg_array),调用未定义方法时调用.__call很有用,但要慎用,因为太灵活.
应用场景:有一个专门打印Person类信息的Person_Writer类,如果通过Person类调用Person_Writer类.
//Person委托Person_Writer类处理打印事务. class Person { private $writer; ... function __call($method_name,$args){ if(methood_exists($this->wirter,$method_name)){ return $this->writer->method_name($this); } } //高级__call写法,当委托方法参数不确定时使用. function __call($method_name,$args){ //当然这里这样写法意义不大,但是call一般都是用call_user_func_array调用 $args = $this ; if(methood_exists($this->wirter,$method_name)){ return call_user_func_array( array($this->writer,$method_name),$args); ) } } }
回调函数应用场景: 3个类,
Product类,Product_Sale类,Product_Totalizer类,要实现:当卖出Product总共价格超过指定金额时,输出警告.
//Product
class Product {
public $name;
public $price;
}
//Product_Sale
class Product_Sale {
private $callbacks;
//记录回调函数
function register_callback ($callback) {
if(! is_callback($callback)){
thow new Exception('callback not callable');
}
$this->callbacks[] = $callback;
}
//执行回调函数
function sale ($product){
print "{$product->name} : 处理中 \n";
foreach($this->callbacks as $callback){
call_user_func($callback , $product);
}
}
}
//Produce_Totalizer
class Produce_Totalizer {
static function warn_amount ($amt) {
$count = 0;
return function ($produce) use ($amt , &count) {
$count += $produce->price;
print " count : {count}\n"
if($count>$amt){
print "超过指定金额{$amt}啦~";
}
};
}
}
//模拟场景
$product_sale = new Produce_Sale();
//指定报警金额为8块
$product_sale = register_callback(Produce_Totalizer::warn_amount(8));
//卖商品
$product_sale->sale(new Product("Durex",6));
$product_sale->sale(new Produce("Jissbon",5));
//输出结果
Durex : 处理中
count :6
Jissbon : 处理中
count: 11
超过指定金额8块啦~
6. `get_class()`和`instanceof`
`get_class(类)`用于判断是否精准等于类名;
`instanceof` 可以判断是否其本身或继承于某父类.
7. 类中的方法和类中的属性
`get_class_methods('类名')`:获取类中所有方法.
`get_class_vars('类名')`:获取类中所有public参数;
8. 反射API
2 模式
2.1 组合
问题:课堂类被演讲类和研讨会类继承着.但是演讲类和研讨类都要实现一次性计费和上N次课计费的方法.和输出计算的方式.
解决方案1: 在课堂类中添加计算一次性付费的方法,上N次课的计费方法和输出计算方式的方法.
解决方案2: 运用组合,将处理计费和输出计算方式单独封装为一个计费策略类.
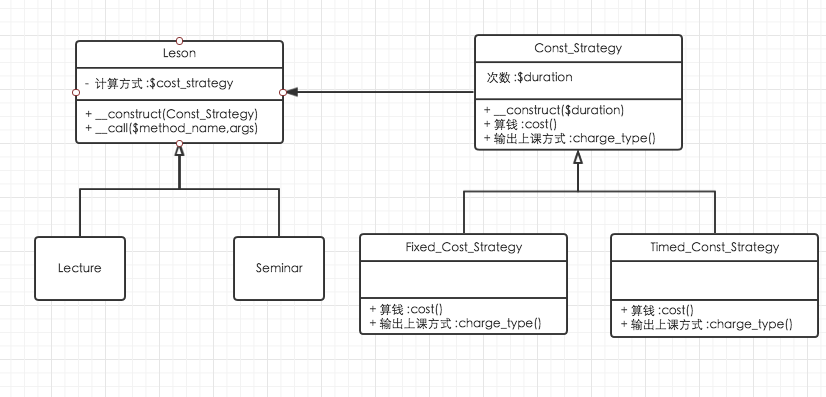
abstract class Cost_Strategy {
protected $duration;
abstract function cost ();
abstract function charge_type();
public __construct($duration){
$this->duration = $duration;
}
}
class Timed_Const_Strategy extends Cost_Stratedy {
function cost () {
//上一次课给5块钱- -.
return $this->duration * 5;
}
function charge_type(){
return "多次课结算";
}
}
class Fixed_Const_Strategy extends Cost_Stratedy {
function cost (){
return 30 ;
}
function charge_type(){
return "一次性课结算";
}
}
abstract class Leason {
private $cost_strategy;
public __construct(Const_Strategy $cost_strategy){
$this->cost_strategy = $cost_strategy;
}
function __call($method_name,$args){
$args = $cost_strategy ;
if(methood_exists($this->cost_strategy,$method_name)){
return call_user_func_array(
array($this->writer,$method_name),$args);
)
}
}
}
//运用
$leasons[] = new Seminar(new Timed_Const_Strategy(4));
$leasons[] = new Lecture(new Fixed_Const_Strategy(null));
foreach ($leasons as $leason){
print "leason charge : {$leason->const()}";
print "charge_type : {$leason->charge_type()}"
}
leason charge 20. charge_type : 多次课结算;
leason charge 30. charge_type : 一次课结算;
组合既委托.同级委托.
继承既父子关系.
3 生成对象
3.1 单例模式
确保系统中只有唯一一个用例.例如系统配置文件.
重点
1: 构造方法私有.
2: 类本身包含自己的实例化属性.
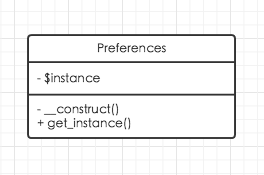
class Preferences {
private static $instance;
private function __construct(){ ... }
public static function get_instance(){
if(empty(self::$instance)){
self::$instance = new Preferences();
}
return self::$instance;
}
...
}
//使用
$preferences = Preferences::get_instance();
3.2 工厂模式
通过一个父类,生产处多个不同功能的子类.
特点:产品方(新浪微博)和需求方(显示新浪微博)一一对应.
问题:印象笔记中,来源可能为新浪微博,或者开发者头条,在印象笔记显示的时候,两者的页眉和页尾是不一样的.
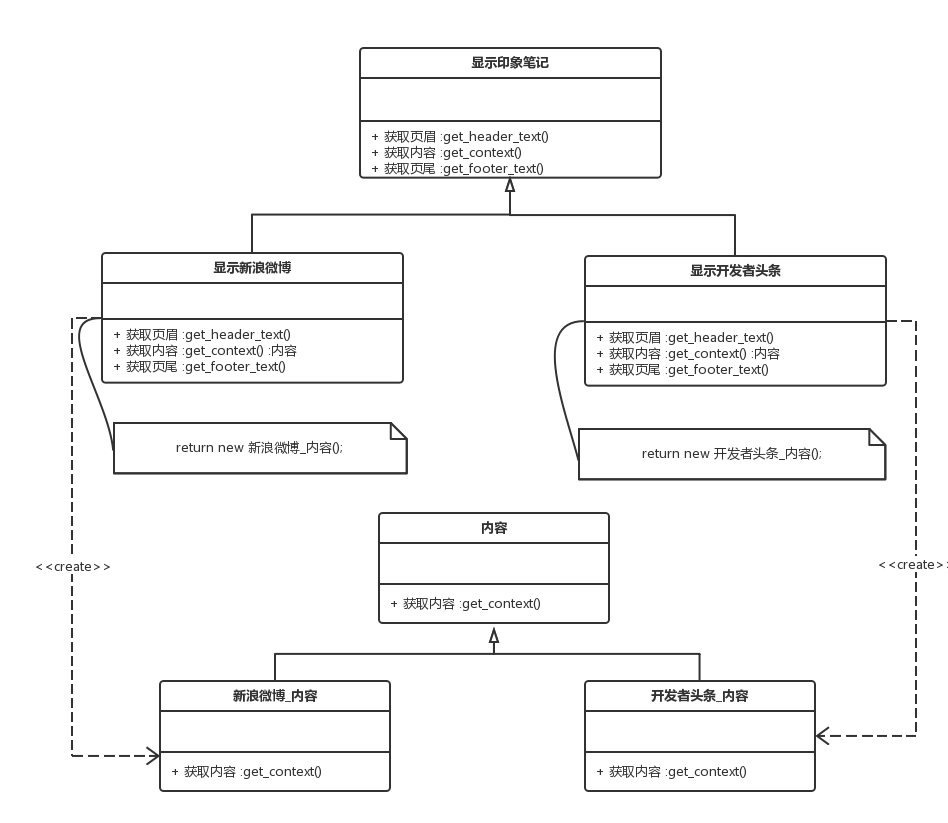
3.3 抽象模式
RLGL!!!.印象笔记不只要显示新浪微博内容!!!还要显示我的新浪账号,还要该微博啊!!卧槽~憋着急,吻我.
工厂模式主要用于生产一一对应的产品方和需求方,而抽象模式要做的是一个需求方(印象笔记_显示新浪微博),要多个工厂(把需求方抽象为多个需求方),例如提供新浪内容的工厂,提供新浪账号的工厂.提供微博内容的评论的工厂等.

代码:
abstract class Show_Evernote {
abstract function get_header_text();
abstract function get_context();
abstract function get_footer_text();
abstract function get_user();
abstract function get_comment();
}
class 显示新浪微博 extends Show_Evernote{
function get_header_text(){...};
function get_context(){new 新浪微博_内容;}
function get_footer_text(){...};
function get_user(){new 新浪微博_账号 ;}
function get_comment(){new 新浪微博_评论;}
}
//使用
印象笔记控件类->内容 = 显示新浪微博->get_context;
印象笔记控件类->账号 = 显示新浪微博->get_context;
...
3.4 平行模式
当使用工厂/抽象模式必须要制定具体的创建者(需求方).
平行模式和抽象模式的模型图一致,但代码实现不一样.
抽象模式中父类均为抽象类,而平行模式中,所以类都为普通类,方便父类的实例化.
在这里列出显示印象笔记类的实现代码
class Show_Evernote{
private $内容;
private $账号;
private $评论;
function __construct(内容,账号,评论){
$this->内容 = 内容;
$this->账号 = 账号;
$this->评论 = 评论;
}
function get_内容(){
return clone $this->内容);
}
function get_账号(){
return clone $this->账号);
}
function get_评论(){
return clone $this->评论;
}
}
//使用
$factory = new Show_Evernote(
new 新浪微博内容(),
new 新浪微博账号(),
new 新浪微博评论()
);
印象笔记控件类->显示印象笔记 = $factory;
其实大家可以发现,原型模式只不过只在最顶层类中包装了一下各组件子类而已,然而这样可以轻松的组合他们,例如实现一个显示新浪微博内容,但要显示开发者头条账号的需求?
4 使用对象
4.1 组合模式
组合模式,可以理解为单一对象管理组合对象(聚合组件),最终组合体下的各个组合部件最好类型一致.不然特殊性越多,需要判断就越多.
假设捶背男,洗脚男,洗发男,用来服务一个人(妹子).
假设妹子的几个部位可用的服务男均为无限个.

//创建一个妹子
$妹子 = new 人();
//添加洗脚男、捶背男
$妹子->add_man(new 洗脚男);
$妹子->add_man(new 捶背男);
//循环所有男的给予舒服的方法.
$妹子->计算舒服程度();
这是一个很理想的组合模式,在现实情况,我们使用组合模式,可能不得不创建多种类型的洗脚男,需要添加许多判断条件.
4.2 装饰模式
装饰模式,首先洗脚男,洗发男,捶背男都是人,但是如果,一个男的又捶背,又洗发,这怎么玩?.add_man两次?这不科学吧,来给这些男的装饰一下吧~

abstract class 人{
...
abstract function get_well();
}
class 男 extends 人 {
//无论你是神马男,服务你,你就能获得10点舒服度.
private $well = 10;
function get_well(){
return $this->well();
}
}
abstract class 装饰男类型 extends 人 {
protected $人;
function __construct(人 $人){
$this->人 = $人;
}
}
class 捶背装饰 extends 类型男装饰{
function get_well(){
return $this->人->get_well()+30;
}
}
class 洗发装饰 extends 类型男装饰{
function get_well(){
return $this->人->get_well()+20;
}
}
class 洗褪装饰 extends 类型男装饰{
//老子不喜欢别人碰我的毛裤.
function get_well(){
return $this->人->get_well()-20;
}
}
//创建捶背,能给予的舒服指数 - -嘻嘻.
$人 = new 捶背装饰(new 男);
$人->get_well(); // 10+30 = 40
//来来来,全能选手,捶背、洗发、洗腿一起来
$人 = new 洗脚装饰(new 洗发装饰(new 捶背装饰(new 男()))); //10+30+20-20 = 40,注意顺序,由里到外执行.
装饰模式,既(组合+继承),基类方法一定要尽量少,不然子类可能有它不该有的方法.直接类继承,她只可能是一种形态,而她的多种形态可能一并拥有的时候,应该运用组合.
继承即单一多态,组合既多种多态.
这个例子中,你可以添加女,然后把装饰男类型改为装饰通用类型,但每个get_well()都要多一个判断是男还是女(如果给予的舒服程度不一样).
这只是确保不可能出现在男,女之外的第三种人,如果基类为动物,给予服务的可能是鸡,鹅,鸭,那么装饰类型应该运用工厂模式,动物形态和装饰形态一一对应.方便拓展.
除了服务类型,服务男的样子也很重要,这就多了一种装饰,现在有装饰男类型和相貌男类型,这种情况怎么破,其实类似.

//如何获取捶背的帅哥麦?,
$人 =new 男类型(new 捶背(new 帅哥麦(new 男())));
4.3 外观模式
即给外部系统提供清晰接口
例如当Model层写得很混乱,但是里面的方法还能用,那我们的Controller层应该列举一些清晰的访问方法来供View层访问.外观模式,强调的是清晰的访问接口.
5 执行任务
5.1 策略模式
给类添加功能.对象要显式的调用它.
继续刚才的洗脚男和人的故事吧...你丫的爽完了要给钱吧?支付宝?微信?现金?
这个付款方式有多种,实现方法不应该放在人类中,而是应该委托给别的类
abstract class 人 {
protectd $支付方式;
function set_支付方式(){...}
function 付款(金额){
return $支付方式->付款($金额);
}
}
abstract class 付款{
abstract function 付款($金额);
}
class 支付宝付款 extends 付款{
function 付款($金额){
return 外接支付宝付款流程($金额);
}
}
...
//使用
$男 =new 男();
///爽爽爽
...
//结账
$支付宝支付账单 = new 支付宝付款($金额);
$人 = new 男();
$人->set_支付方式(new 支付宝付款());
$人->付款();
5.2 观察者模式
当被观察者发生变化,观察者需要被通知.
当数据发生变化,页面需要被通知.
使用步骤:
- 观察者加载到被观察者中.
- 被观察者通知观察者.
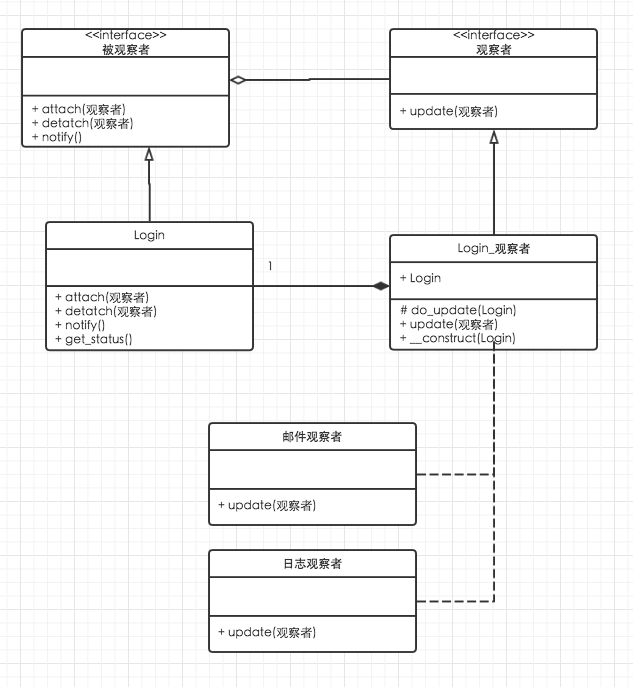
例如登陆类(被观察)状态改变,要出发邮件系统和日志系统(观察者)
interface 被观察者{
function attach(观察者);
function detatch(观察者);
function notify();
}
class Login implements 被观察者{
private $观察者;
function __construct(){
$this->观察者 = array();
}
function attach($观察者){
$this->观察者 = $观察者;
}
function detach($观察者){
//删除某个观察者的操作;
}
function notify(){
foreach ($this->观察者 as $单个观察者){
$单个观察者->update($this);
}
}
}
interface 观察者{
function update(被观察者);
}
abstract class Login_观察者 implements 观察者{
private $login;
function __construct (Login $login){
$this->login = $login;
$login->attach($this);
}
function update(观察者 $观察者){
if ($观察者 ===$this->login){
$this->do_update($观察者);
}
}
abstract function do_update(Login $login);
}
class 邮件观察者 extends 登陆观察者 {
function do_update(Login $login){
//判断条件 发送邮件
}
}
class 日志观察者 extends 登陆观察者 {
function do_update(Login $login){
//判断条件 记录到日志;
}
}
//使用
$login = new Login();
new 邮件观察者 ($login);
new 日志观察者 ($login);
PHP有内置的SPL实现上述的观察者模式.
5.3 访问者模式
问题: 在一个军队中,有很多军队,军队下面可能包含军队/步兵/弓箭手,这时我们要显示一个军队的战斗力/需要粮食的各级分配?(遍历对象并设置显示方法).怎么办?.解决办法是军队还是保存自己的基本信息,设置一个访问者,访问者包含总战斗力方法和总粮食的方法.
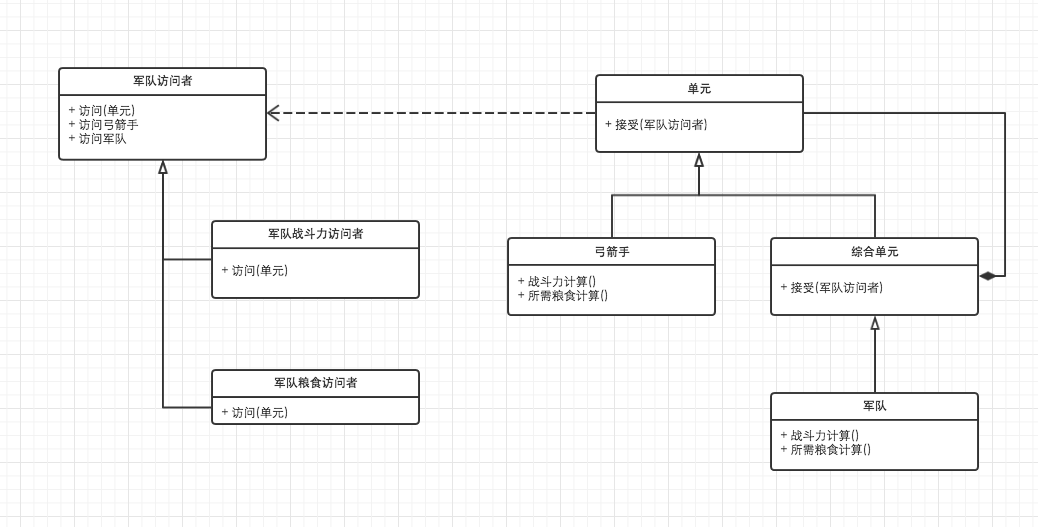
访问者
abstract class 军队访问者{
abstract function 访问(单元);
function 访问军队($军队){
$this->访问($军队);
}
function 访问弓箭手($弓箭手){
$this->访问($弓箭手);
}
//这里重复定义了大量代码,其实可以用call来替代
function __call($method_name,$args){
if(strrpos($method_name, "访问")){
return call_user_func_array(
array($this,"访问"),$args
);
}
}
}
class 军队战斗力访问者 extends 军队访问者{
private $text="";
function 访问($单元){
$ret = "";
$pad = 4*$单元->getDpth(); //设置显示深一级前面多4个空格.
$ret .= sprintf( "%{$pad}s","");
$ret .= get_class($单元). ": ";
$ret .= "战斗力: " .$单元->bombardStrenth()."\n";
$this->text .=$ret;
}
function get_text(){
return $this->text;
}
}
被访问者
abstract class 单元{
function 接受($军队访问者){
$method = "访问_".get_class($this);
$军队访问者->$method($this);
}
private $depth;
protected function set_depath($depth){
$this->depth=$depth;
}
function get_depth(){
return $this->depth;
}
...
}
abstract class 综合单元 extends 单元{
function 接受($军队访问者){
parent::接受($军队访问者)
foreach($this->单元集合 as $this_unit){
$this->unit->接受($军队访问者);
}
}
}
class 军队 extends 综合单元{
function bombardStrenth(){
$ret =0;
foreach($this-units() as $unit){
$ret += $unit->bombardStrenth();
}
return $ret
}
}
class 弓箭手 extends 单元{
function bombardStrenth(){
return 4;
}
}
调用
$main_army = new Army();
$main_army->add_unit(new 步兵());
$main_army->add_unit(new 弓箭手());
$军队战斗力访问者_实例 =new 军队战斗力访问者();
$main_army->接受(均分战斗力访问者);
print $军队战斗力访问者->get_text();
输出
军队: 战斗力: 50
步兵: 攻击力 :48
弓箭手: 攻击力: 4
5.4 命令模式
例子为Web页面的login和feed_back,假如都需要使用ajax提交,那么问题来了,将表单封装好提交上去,得到了返回结果.如何根据返回结果跳转不同的页面?.
有些同学就说了,login和feed_back各自写一个方法憋,提交的时候调用各自的方法.
然后再来个logout命令..增加..删除..命令怎么办..
命令模式比较适合命令执行例如登陆,反馈等简单只需要判断是否成功的任务
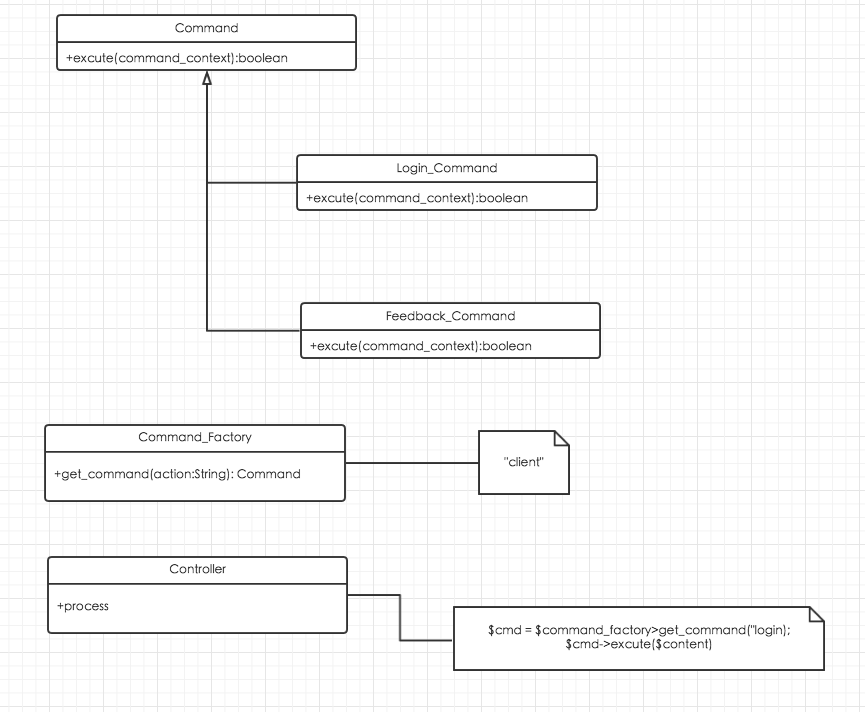
命令:
abstract class Command{
abstract function execute(Conmmand_Context $context);
}
class Login_Command extends Command{
function execute(CommandContext $context){
$managr =Register::getAccessManager();
$user = $context->get("username");
$pass = $context->get('pass');
$user_obj = $manager->login($user,$pass);
if(is_null($user_obj)){
$context->setError($manager->getError());
return false;
}
$context->addParam("user",$user_obj);
return true;
}
}
部署命令的调用者
class Command_Facotry{
public function get_command($action){
$class = UCFirst(strtolower($action))."_Command";
$cmd = new $class();
return $cmd;
}
}
客户端
class Controller{
private $context;
function __construct(){
//Command_Context主要用来存储request和params
$this->context =new Command_Context();
}
function process(){
$cmd Command_Factory::get_commad($this->context->get('action'));
if(!$cmd-execute($this->context)){
//错误处理
}else{
//成功 分发视图
}
}
}
使用
$controller =new Controller();
$context = $controller->get_context();
$context->add_param('action','login');
$context->add_param('username','404_k');
$context->add_param('pass','123456');
$controller->process();